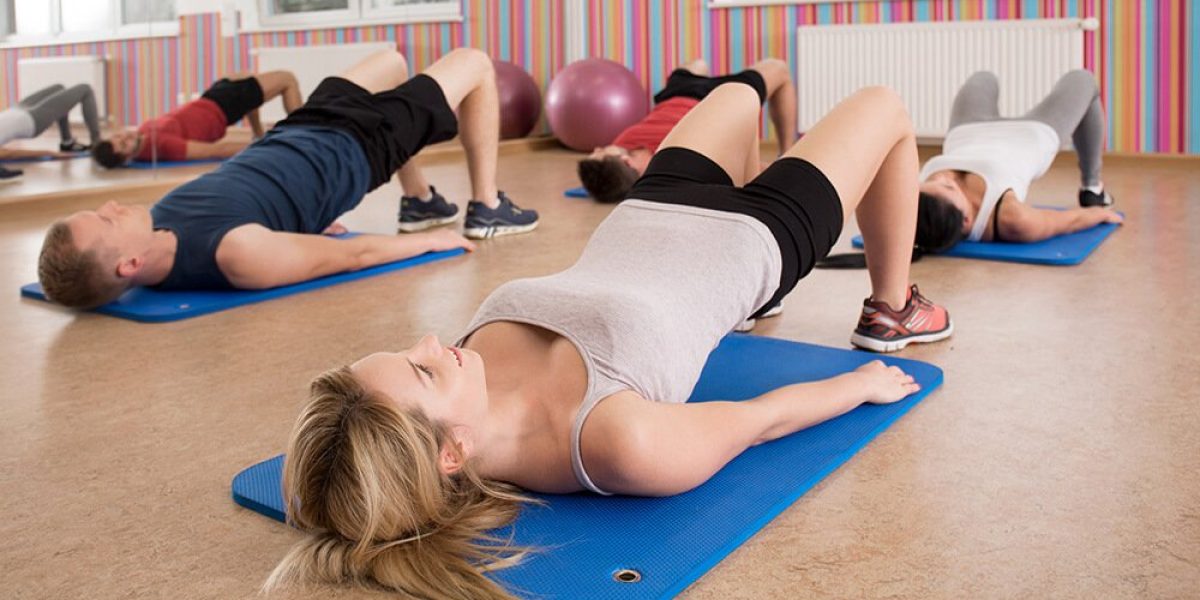
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
Before diving into how exercise can help, it’s essential to understand what erectile dysfunction is. ED is defined as the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It’s not unusual for men to occasionally experience difficulty with erections, especially under stress or fatigue, but chronic issues could indicate an underlying health concern. Cenforce 100 and Cenforce 200 are two that are effective against ED.
Common causes of ED include:
-
Poor blood circulation
-
High blood pressure
-
Diabetes
-
Obesity
-
Low testosterone
-
Psychological factors (stress, anxiety, depression)
-
Smoking and excessive alcohol use
-
Sedentary lifestyle
Many of these risk factors overlap with broader cardiovascular and metabolic health concerns, and that’s exactly where exercise comes in.
The Link Between Exercise and Sexual Health
1. Improved Blood Flow
Erections are all about blood flow. When a man becomes sexually aroused, blood rushes into the penile tissues, creating an erection. If circulation is poor, due to clogged arteries, high blood pressure, or other cardiovascular issues, the result is often weak or nonexistent erections.
Exercise helps maintain the health of blood vessels and improves blood flow throughout the body. Aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming strengthen the heart and promote better circulation. Over time, this can significantly reduce ED symptoms.
2. Hormonal Balance and Testosterone Boost
Low testosterone is a common cause of reduced libido and ED. Exercise, especially strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), has been shown to boost testosterone levels naturally.
Additionally, exercise reduces levels of cortisol, the stress hormone that can suppress testosterone production, and promotes the release of endorphins and dopamine, hormones associated with pleasure and reward. This hormonal balance plays a critical role in enhancing libido and sexual performance.
3. Weight Loss and Body Composition
Obesity, particularly central obesity (belly fat), is closely linked to ED. Fat cells, especially those in the abdomen, convert testosterone into estrogen, reducing male hormone levels. Carrying excess weight also increases inflammation and the risk of conditions like diabetes and hypertension both of which are major contributors to ED.
Exercise is a cornerstone of effective weight loss and weight management. Regular physical activity helps burn fat, build lean muscle, and reduce insulin resistance, creating a more favorable environment for sexual function.
4. Mental Health and Confidence
Psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem often go hand in hand with erectile dysfunction. Worrying about performance can itself cause ED, creating a vicious cycle.
Exercise is a powerful tool for mental health. It reduces anxiety, improves mood, and boosts self-confidence. Physically active men are less likely to report symptoms of depression and more likely to feel confident about their bodies, all of which can lead to better sexual experiences.
What Types of Exercise Help with ED?
Not all exercise is created equal, but a variety of physical activities can improve erectile function. Here are some of the most effective:
1. Aerobic Exercise
-
Examples: Walking, running, cycling, swimming, dancing
-
Benefits: Improves cardiovascular health, reduces blood pressure, boosts circulation
-
How often: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week
2. Resistance Training
-
Examples: Weightlifting, bodyweight exercises, resistance bands
-
Benefits: Increases testosterone, reduces fat, builds confidence
-
How often: 2–3 sessions per week targeting major muscle groups
3. Kegel Exercises
-
What they are: Exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which are directly involved in erections and ejaculation.
-
How to do them: Identify the right muscles (try stopping urination midstream — that’s your pelvic floor), contract and hold for a few seconds, then release. Repeat 10–15 times, 3 times per day.
-
Benefits: Enhances erection strength and control, may help with premature ejaculation
4. Yoga and Stretching
-
Benefits: Increases flexibility, reduces stress, improves circulation
-
Bonus: Some poses, like the cobra and bridge pose, specifically target pelvic muscles and blood flow to the groin area
How Quickly Can You See Results?
While the benefits of exercise compound over time, some improvements in ED symptoms can be seen in as little as a few weeks, depending on the severity of the condition and consistency of your efforts. One 2018 study published in the Sexual Medicine journal found that men who engaged in moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise four times per week for six months experienced significant improvements in erectile function.
However, it’s essential to pair exercise with other healthy habits for best results, such as:
-
Eating a heart-healthy diet (e.g., Mediterranean or DASH diet)
-
Reducing alcohol and quitting smoking
-
Managing stress
-
Getting quality sleep
Final Thoughts: A Natural, Empowering Solution
Erectile dysfunction is often seen as a purely physical or age-related problem, but the truth is more nuanced. It’s a multifactorial issue that reflects your overall health. The good news? That means there’s a lot within your control — and exercise is one of the most powerful tools at your disposal.
By improving circulation, boosting testosterone, enhancing mood, and reducing key risk factors, regular physical activity can significantly improve sexual function and quality of life. It’s safe, cost-effective, and offers a host of additional health benefits. While it may not replace medical treatment in all cases, it should absolutely be part of the conversation — and the routine — for any man looking to overcome ED naturally.