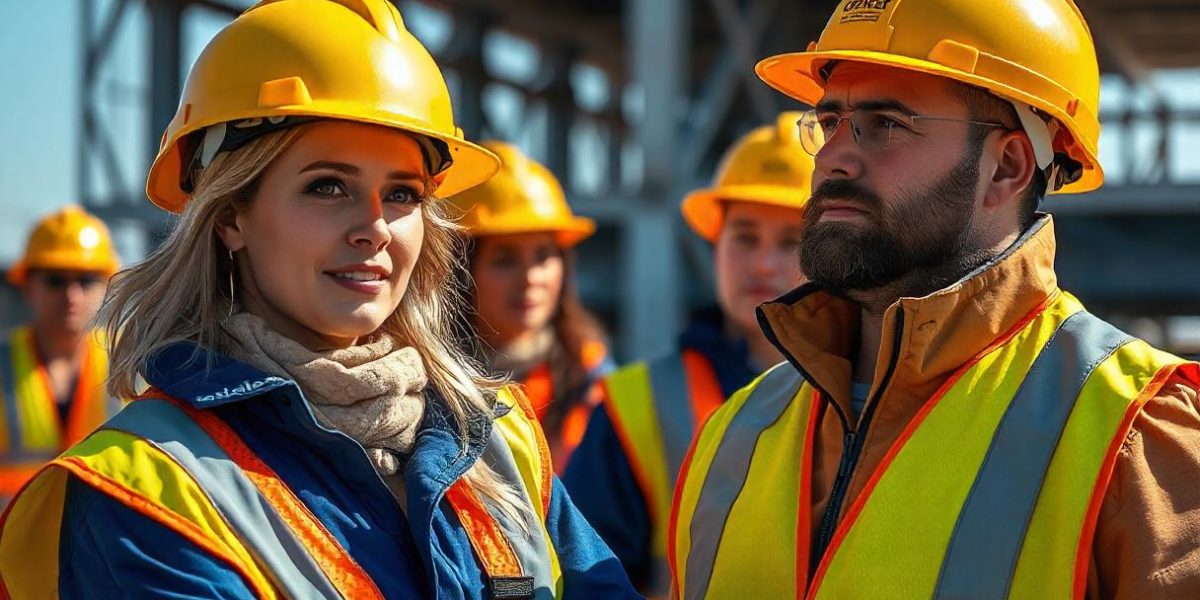
Working in hot conditions can be extremely challenging, especially for those in industries like construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and warehousing. Heat stress is a serious workplace hazard that can lead to severe health problems, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke. If not managed properly, excessive heat can decrease productivity, increase workplace accidents, and even result in life-threatening conditions.
In this article, we will explore the dangers of heat stress, real-life examples of workers affected by extreme heat, and practical steps to stay safe and hydrated at work. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to prevent heat-related illnesses and ensure a safer working environment. Enrolling in a Safety Course in Multan can provide essential knowledge and training to help workers effectively manage heat stress and other workplace hazards.
Understanding Heat Stress: Why It’s a Workplace Hazard
Heat stress occurs when the body is unable to regulate its temperature effectively due to excessive heat exposure. This condition is common in workplaces where employees engage in physical labor under high temperatures, humidity, or direct sun exposure.
Symptoms of Heat Stress
Workers exposed to extreme heat may experience:
- Excessive sweating
- Dizziness and confusion
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Muscle cramps
- Fainting
Ignoring these signs can lead to serious health problems such as heat exhaustion or heatstroke, which require immediate medical attention.
Real-Life Example: The Hidden Danger of Heat Stress
Mark, a construction worker, was working on-site during a hot summer afternoon. Despite feeling lightheaded and weak, he continued working, assuming it was just normal fatigue. Within minutes, he collapsed due to heat exhaustion and had to be rushed to the hospital. His employer later introduced heat stress management policies, including mandatory breaks, shade provisions, and hydration stations to prevent such incidents in the future.
Step-by-Step Guide to Prevent Heat Stress at Work
Preventing heat stress in the workplace is not just the employer’s responsibility; workers must also take proactive measures. Below is a step-by-step guide to reducing heat-related illnesses and improving workplace safety.
Step 1: Stay Hydrated Throughout the Day
One of the most effective ways to prevent heat stress is to drink enough water. Dehydration increases the risk of heat-related illnesses and reduces physical performance.
Hydration Tips:
- Drink water every 15–20 minutes, even if you’re not thirsty.
- Avoid sugary or caffeinated beverages as they contribute to dehydration.
- Consume electrolyte-rich drinks to replenish lost minerals from sweating.
- Set hydration reminders to ensure you drink regularly.
Step 2: Take Frequent Breaks in Shaded Areas
When working in extreme heat, it is essential to take breaks in cool or shaded areas to lower body temperature.
Workplace Adjustments:
- Employers should provide cooling stations or shaded break areas.
- Workers should take breaks every hour in high temperatures.
- Wearing a cooling vest or using cold compresses can help regulate body temperature.
Step 3: Wear Proper Clothing and Protective Gear
What you wear at work can significantly impact your body’s ability to handle heat.
Recommended Work Attire:
- Lightweight, loose-fitting, and light-colored clothing.
- Moisture-wicking fabrics to absorb sweat and keep you cool.
- Wide-brimmed hats to protect from direct sun exposure.
- UV-protection sunglasses to shield eyes from harsh sunlight.
Step 4: Recognize and Respond to Early Signs of Heat Stress
Being aware of the early symptoms of heat stress can prevent severe health issues.
What to Do If You Notice Symptoms:
- Stop work immediately and move to a cool area.
- Drink cool water or electrolyte drinks.
- Apply cooling towels or ice packs to the body.
- If symptoms persist, seek medical attention immediately.
Step 5: Train Workers on Heat Stress Prevention
Employers should conduct heat stress safety training to educate workers about the risks and prevention strategies.
Essential Training Topics:
- How to recognize heat stress symptoms.
- The importance of proper hydration and breaks.
- Emergency response procedures for heat-related illnesses.
Step 6: Implement Workplace Policies for Heat Safety
Companies should adopt heat stress prevention policies to create a safer work environment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Adjust work schedules to avoid peak heat hours.
- Provide cooling fans or air-conditioned rest areas.
- Encourage workers to use the buddy system to monitor each other’s health.
- Supply hydration stations in high-temperature work zones.
The Importance of Workplace Safety Training
Investing in a Safety Course in Multan can equip workers with essential knowledge on preventing heat stress and other workplace hazards. Safety training programs cover topics like personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency response, and occupational health risks, ensuring a safer work environment for employees.
Read More: Find Affordable Safety Officer Diploma Here
Final Thoughts
Heat stress is a serious occupational hazard that requires immediate attention. By implementing proper hydration strategies, adjusting work schedules, and conducting safety training, employers can significantly reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses in the workplace.
Workers should also take responsibility by staying hydrated, recognizing early symptoms, and following workplace safety guidelines. A safe and heat-conscious work environment leads to increased productivity, fewer injuries, and a healthier workforce.
How does your company handle heat stress prevention? Share your thoughts in the comments below!