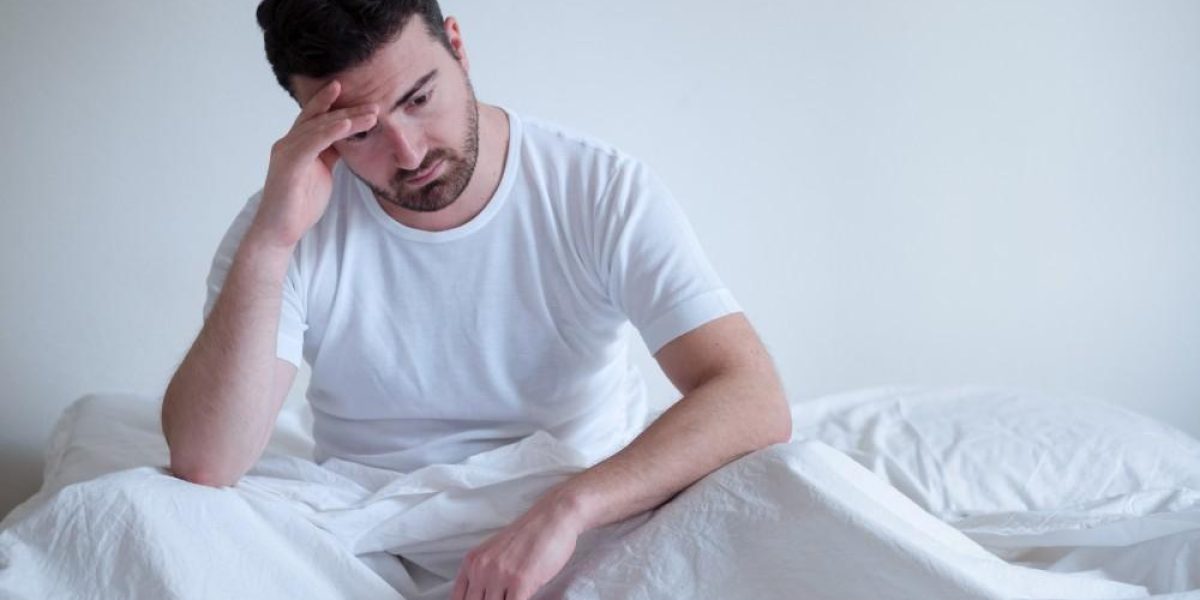
Libido, often referred to as sexual desire or drive, is a fundamental aspect of human sexuality that impacts overall well-being and relationships. It reflects a person’s interest in sexual activity and can be influenced by a variety of physical, emotional, and psychological factors. In men, libido is closely connected to hormonal balance, neurological function, and cardiovascular health. A healthy libido contributes not only to sexual satisfaction but also to emotional intimacy and self-esteem. When libido decreases significantly or disappears, it can lead to distress, frustration, and problems in intimate relationships.
Causes of Low Libido in Men:
Andrology: Lack Of Libido in Dubai (علاج نقص الرغبة الجنسية في دبي) in men can arise from a complex interplay of biological and psychological factors. Hormonal imbalances, especially low testosterone levels, are among the most common physical causes. Testosterone plays a crucial role in regulating sexual desire, and when its levels drop, libido often declines. Other physical causes include chronic illnesses such as diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders. Medications for various conditions, including antidepressants and blood pressure treatments, may also reduce sexual desire. Psychological contributors such as stress, anxiety, depression, and unresolved relationship conflicts frequently play a significant role in diminishing libido.
The Role of Hormones in Sexual Desire:
Hormones are vital regulators of sexual desire. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, directly influences libido by acting on the brain and reproductive organs. Besides testosterone, other hormones like prolactin, thyroid hormones, and cortisol can impact sexual function. Elevated prolactin or thyroid imbalances can reduce libido, while high cortisol levels, often a result of stress, suppress sexual desire. Hormonal fluctuations can be triggered by aging, medical conditions, or lifestyle factors, leading to a notable decrease in sexual interest. Understanding the hormonal aspect is essential for identifying and managing low libido effectively.
Psychological Factors Affecting Libido:
Psychological health is intricately linked to sexual desire. Stressful life events, work pressure, anxiety, and depression can all contribute to reduced libido. Mental health disorders not only lower sexual interest but also affect the quality of sexual performance, which can create a negative cycle of frustration and avoidance. Additionally, past traumatic experiences or negative sexual experiences may cause long-term issues with desire. Relationship dynamics, including communication problems and emotional distance, also play a crucial role. Addressing psychological factors is vital for restoring a healthy libido.
Lifestyle Influences on Sexual Desire:
Modern lifestyle choices can significantly impact libido. Poor diet, lack of exercise, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and inadequate sleep are known to reduce sexual desire. Sedentary behavior and obesity contribute to hormonal imbalances and reduced cardiovascular health, which directly affect sexual function. Stress management is another important factor, as chronic stress elevates cortisol, which suppresses libido. Healthy lifestyle changes, including balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, limiting alcohol, quitting smoking, and ensuring sufficient sleep, can improve overall sexual health and reignite sexual desire.
Recognizing Symptoms and Signs of Low Libido:
Low libido may present differently in men depending on the underlying causes and individual differences. Common signs include a reduced interest in sexual activities, lack of spontaneous sexual thoughts or fantasies, diminished sexual excitement, and sometimes difficulty in achieving or maintaining erections. Men might also experience emotional symptoms such as irritability, mood swings, or feelings of inadequacy related to sexual performance. Recognizing these signs early is important for seeking appropriate interventions and preventing further psychological or relational complications.
Approaches to Managing and Improving Libido:
Managing low libido involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and psychological aspects. Lifestyle adjustments aimed at improving diet, exercise, sleep, and stress levels can have a substantial impact. Hormonal evaluations and treatments might be necessary when imbalances are identified. Psychological support, including counseling or therapy, can help address emotional issues, reduce anxiety, and improve communication within relationships. Open conversations with partners about sexual needs and concerns also contribute to restoring intimacy and desire. Overall, improving libido is often achievable through a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion:
Lack of libido is a common and often complex issue that can affect many men at various stages of life. Understanding that sexual desire is influenced by a combination of hormonal, psychological, lifestyle, and relationship factors is crucial for effectively addressing it. Recognizing the signs early and adopting a holistic approach—focusing on both physical health and emotional well-being—can significantly improve sexual desire and overall quality of life. With patience and the right strategies, it is possible to regain a healthy libido and enjoy fulfilling intimate relationships once again.