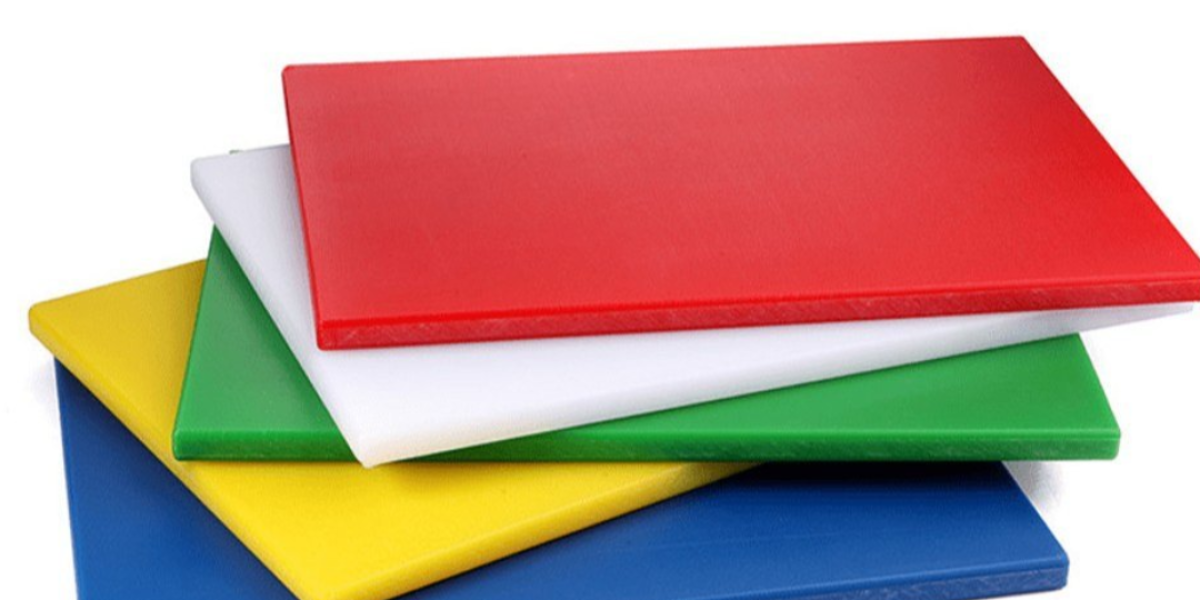
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) sheets are among the most durable and versatile materials used across various industries. Known for their outstanding strength, chemical resistance, and lightweight nature, HDPE sheets have become indispensable in sectors ranging from construction and manufacturing to agriculture and food processing. HDPE, a type of polyethylene plastic, is prized for its resistance to moisture, wear, and chemicals, making it an excellent option for both indoor and outdoor applications. In this Mahira Polyglobal LLP, we will explore the properties, benefits, applications, and versatility of HDPE sheets, highlighting why they are a top choice for many professionals.
What is High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a polymer made from the polymerization of ethylene, a type of hydrocarbon. It is a member of the polyethylene family but differs from its counterparts like Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) due to its molecular structure. HDPE has a higher density and more crystalline structure, resulting in a stiffer, stronger, and more rigid material. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications where toughness and durability are paramount.
HDPE is a thermoplastic, meaning it can be reheated and molded into various forms without losing its integrity. The plastic is highly resistant to chemicals, moisture, and extreme temperatures, which enhances its versatility. HDPE is typically used in sheet form but can also be produced as rolls, offering flexibility depending on the specific application.
Benefits of Using HDPE Sheets
The popularity of Plastic HDPE Sheetss across industries can be attributed to the numerous advantages they offer. Below are the key benefits that make HDPE an excellent choice for various applications:
- Durability: HDPE is incredibly durable, offering resistance to impacts, abrasions, and environmental factors like UV rays. This makes it ideal for both indoor and outdoor use, where materials must withstand rough handling and harsh conditions.
- Chemical and Corrosion Resistance: One of the standout features of HDPE sheets is their exceptional resistance to chemicals and corrosion. HDPE does not degrade easily when exposed to acids, alkalis, or oils, which is why it is often used in chemical tanks, pipes, and containers.
- Water Resistance: HDPE sheets are non-porous, meaning they do not absorb water. This makes them ideal for use in environments exposed to moisture, such as marine applications, pipelines, and food processing environments. It also means they will not rust or degrade like metals.
- Lightweight: Despite their strength, HDPE sheets are lightweight, which makes them easier to handle, transport, and install. This is particularly important in large-scale applications where ease of installation can save both time and labor costs.
- Eco-Friendly: HDPE is 100% recyclable, which makes it an environmentally friendly option. Recycled HDPE can be used to create new products, reducing waste and promoting sustainability in industries that prioritize eco-friendly materials.
- Easy to Fabricate: HDPE sheets can be easily cut, welded, and thermoformed to meet specific needs. This ability to customize the material allows it to be adapted to a wide range of applications.
Common Applications of HDPE Sheets
Given their impressive properties, HDPE sheets are used in a wide array of industries and applications. The following are some of the most common uses for HDPE sheets:
- Construction: HDPE sheets are widely used in the construction industry for applications such as vapor barriers, waterproof membranes, and protective liners for landfills. Their resistance to moisture, chemicals, and physical wear makes them highly effective in these environments.
- Packaging: In the packaging sector, HDPE sheets are used to create durable containers, bottles, and packaging films. Their strength and chemical resistance make them an excellent choice for both food and non-food packaging, ensuring that products remain safe and secure during transportation.
- Food Processing and Storage: HDPE is a non-toxic, FDA-approved material, making it a popular choice in the food industry. HDPE sheets are used to create cutting boards, food containers, and storage bins. They are easy to clean and sanitize, preventing the growth of bacteria and ensuring food safety.
- Marine Applications: Due to its resistance to water and UV radiation, HDPE is commonly used in the marine industry for products like boat hulls, docks, and pontoons. It is also used in the construction of floating platforms and watercraft components.
- Agriculture: In agriculture, HDPE sheets are used for greenhouse covers, irrigation pipes, and pond liners. The material’s resistance to moisture and durability in agricultural environments makes it ideal for such applications.
- Industrial Equipment: HDPE sheets are also used in the manufacturing of industrial components such as conveyor belts, wear strips, and machine guards. Their toughness and ability to withstand heavy-duty use make them suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
HDPE Sheets vs. Other Types of Polyethylene Sheets
While HDPE sheets are a form of polyethylene plastic, it’s important to distinguish them from other polyethylene materials such as Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE). The key difference lies in their molecular structure and density.
LDPE and LLDPE are more flexible and have lower densities compared to HDPE, which means they are more suited for applications that require flexibility, like plastic bags, shrink films, and flexible packaging. In contrast, HDPE’s higher density gives it greater strength, rigidity, and resistance to stress, making it more suitable for heavy-duty applications that require durability and resistance to chemicals and harsh environmental conditions.
In terms of polyethylene sheets, HDPE sheets are the strongest and most durable option. While all polyethylene sheets share certain characteristics, HDPE is preferred for applications that demand long-lasting performance, including industrial, marine, and construction uses.
Polyethylene Roll: A Flexible Alternative
In addition to HDPE Sheets plastic, polyethylene is also available in rolls, offering greater flexibility in terms of application. Polyethylene rolls are often used in packaging, agriculture, and construction. They are typically lightweight, flexible, and can be unrolled to cover large areas. Polyethylene rolls are particularly useful in applications such as greenhouse covers, vapor barriers, and agricultural liners.
The flexibility of polyethylene rolls makes them easy to handle and cut to size, offering adaptability in large-scale projects. Unlike rigid HDPE sheets, polyethylene rolls are more suitable for applications where continuous coverage or flexible, lightweight material is required.
How to Fabricate and Handle HDPE Sheets
Fabricating HDPE sheets is relatively easy compared to other materials. HDPE can be easily cut, welded, and thermoformed into various shapes and sizes to meet specific requirements. The material can be worked with using standard fabrication techniques and tools, such as:
- Cutting: HDPE sheets can be cut using saws, routers, or CNC machines. It is essential to use the right cutting tools to avoid cracking and to achieve clean, precise cuts.
- Welding: HDPE can be welded using techniques such as hot air welding, extrusion welding, or butt welding. This allows for strong, seamless joints between sheets, ensuring structural integrity.
- Thermoforming: HDPE sheets can be heated and molded into custom shapes using thermoforming. This process is commonly used to create containers, trays, and other molded products.
- Storage and Handling: When storing HDPE sheets, it is important to keep them in a cool, dry environment to prevent warping or degradation. Handling the material with care during transportation is also essential to prevent scratches or surface damage.
Conclusion
The Polyethylene high density sheet offer a combination of strength, versatility, and resistance to harsh conditions that make them a preferred material across multiple industries. From construction and manufacturing to food processing and agriculture, HDPE sheets continue to provide reliable, long-lasting performance. Whether used as rigid sheets or flexible polyethylene rolls, HDPE is a durable and cost-effective material that ensures quality and efficiency in a wide range of applications.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainable materials, HDPE’s recyclability and environmental benefits make it an even more attractive option for the future. Its strength, durability, and adaptability ensure that HDPE will remain a go-to material for countless applications across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes HDPE more durable than other plastics?
HDPE has a higher density and more crystalline structure than other types of polyethylene, making it stronger, more rigid, and more resistant to stress, impacts, and environmental factors.
Is HDPE safe for food contact?
Yes, HDPE is FDA-approved for food contact and is commonly used for food containers, cutting boards, and storage bins in the food processing industry.
How do polyethylene rolls differ from HDPE sheets?
Polyethylene rolls are flexible and can be unrolled for continuous coverage, while HDPE sheets are rigid and are used in applications that require strength and durability.
Can HDPE sheets be recycled?
Yes, HDPE is 100% recyclable and can be reused to create new products, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.